Beyond Locomotion for Legged Robots
Abstract
Quadrupeds are rapidly gaining popularity in various applications. Although locomotion of quadrupeds has been extensively researched, there has been limited exploration into enhancing their capabilities beyond walking and running. One such capability observed in nature is the use of legs as manipulators to interact with objects in the environment, such as pushing buttons or grabbing objects. This project aims to enable this capability in quadrupeds through reinforcement learning (RL) and then dividing the problem into smaller subproblems. Separate RL policies can be trained for specific subproblems, such as locomotion (moving from point A to point B) and manipulation (e.g., pushing buttons while standing still). A higher-level decision algorithm will then be employed to select between these policies, similar to the approach introduced by Cheng et al. [1]. IsaacGym [2] is used for the simulation platform to accelerate the learning algorithm
Introduction
Quadruped robots offer versatility, handling a range of tasks from environmental mapping to military applications. These robots have advanced in locomotion capabilities, yet all four legs could also serve as manipulators, performing actions beyond simple movement. This project establishes a framework to enable quadrupeds to perform manipulation tasks using one leg as an arm.

Background
Reinforcement Learning
The RL problem, modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), involves optimizing reward by mapping states to actions through a policy (Π). Key components include the state (S), action (A), and reward function (R). The Q-function guides action selection by estimating cumulative rewards from a given state-action pair.
Methods
This project employs IsaacGym [2] to create a training environment, initializing multiple Unitree B1 robots for parallel training. Observations are mapped to a 48-dimensional space covering the robot’s position, orientation, joint acceleration, and velocity, while the 12-dimensional action space outputs joint angles.
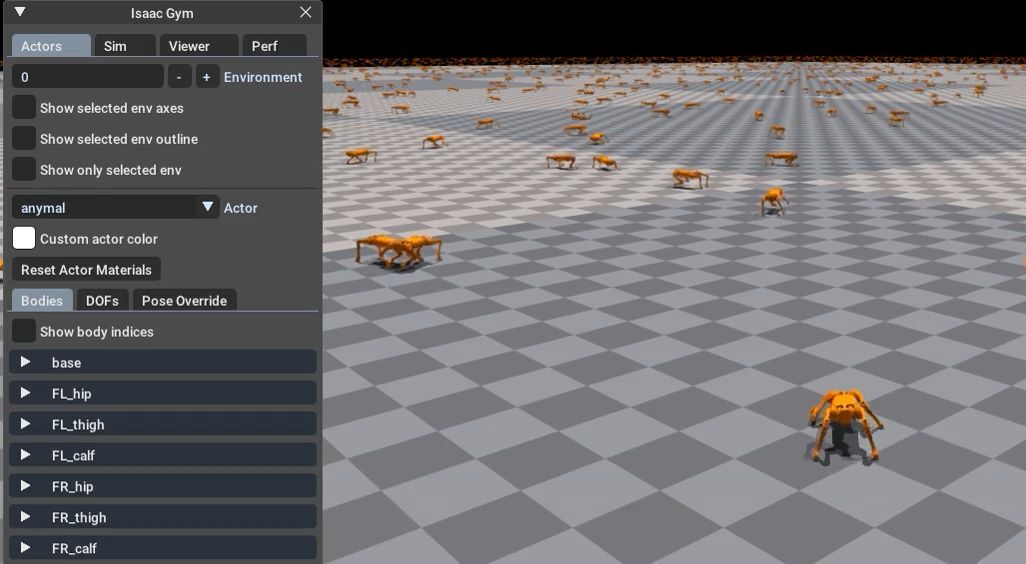

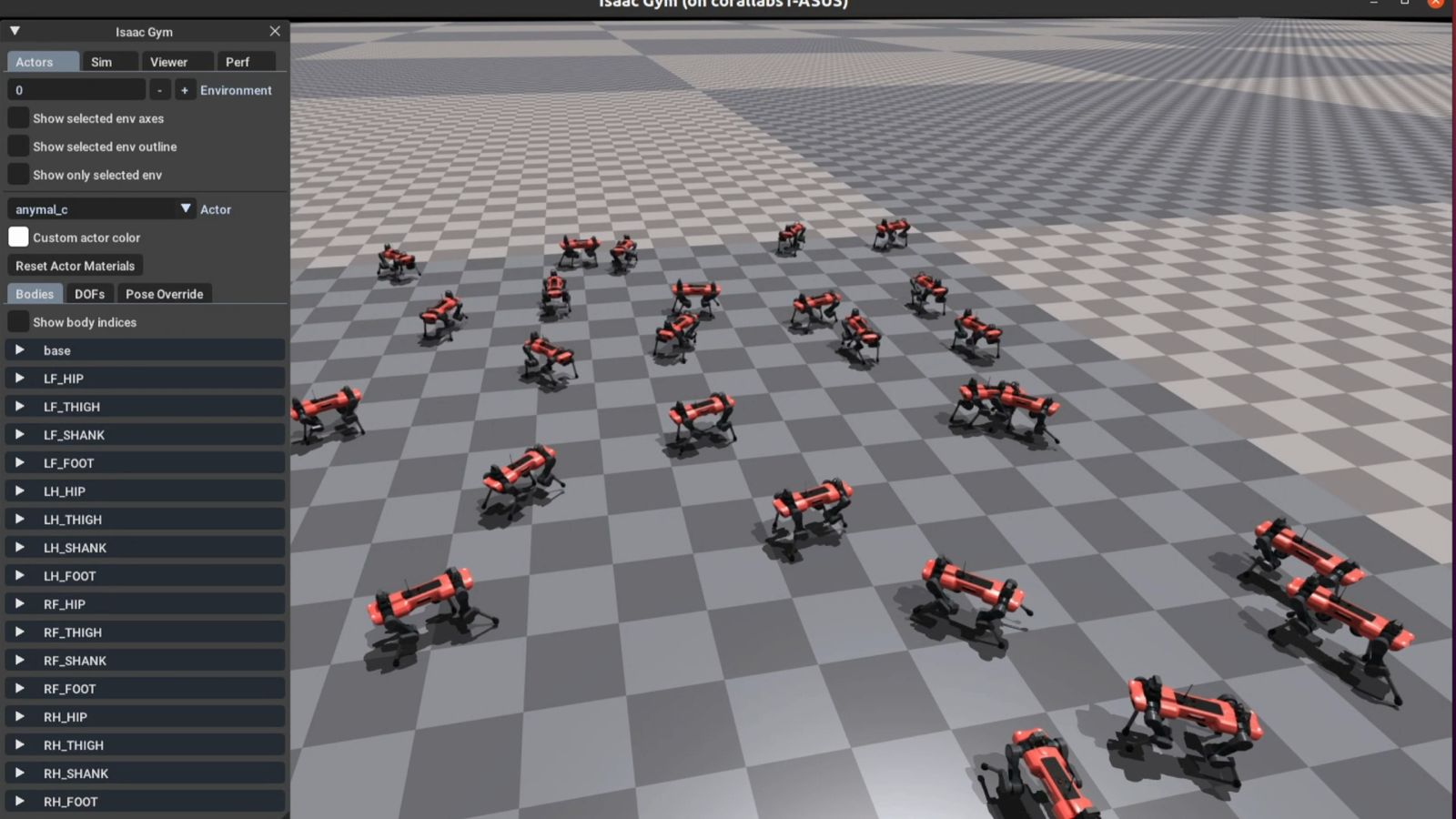
Simulation Setup
IsaacGym was set up with 4096 B1 robots on a plane. Several repositories, including IsaacGymEnvs, legged gym, and extreme-parkour, provided tools and configurations for quadruped RL tasks.
Conclusion
This project accomplished foundational steps, including IsaacGym setup and locomotion policy development for Unitree B1. Future work could improve walking dynamics and integrate manipulation for more complex tasks.
Future Work
- Training a Manipulation Policy for leg control in manipulation tasks.
- Refining Locomotion Policy to achieve smoother walking in B1.
- Task Integration: Implement tasks that combine locomotion and manipulation.
References
- Cheng, X., Kumar, A., Pathak, D., Legs as Manipulator: Pushing Quadrupedal Agility Beyond Locomotion, ICRA 2023.
- Makoviychuk, V., et al., Isaac Gym: High Performance GPU-Based Physics Simulation For Robot Learning, arXiv, 2021.
- Cheng, X., Shi, K., Agarwal, A., Pathak, D., Extreme Parkour with Legged Robots, arXiv, 2023.
- Reinforcement learning, Wikipedia.
- Rudin, N., Hoeller, D., Reist, P., Hutter, M., Learning to walk in minutes using massively parallel deep reinforcement learning, arXiv, 2021.