Beginners Guide to Re-enforcement Learning
Parth Patil, 170070011
This is a tutorial hosted as a part of course assignment of GNR638: Machine Learning for Remote Sensing - II
This tutorial will help you to learn the basics of Re-enforcement Learning, how it is useful, along with a real-life example. This tutorial has no prerequisites as such, but knowing about the Machine Learning, Neural Network will surely help you to understand better.
Introduction
So firstly what is Re-enforcement Learning? The Google definition says the following.
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an area of machine learning concerned with how software agents ought to take actions in an environment so as to maximize some notion of cumulative reward. Reinforcement learning is one of three basic machine learning paradigms, alongside supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
In simple terms, it a branch of machine learning where the software agent tries to learn to interact with its environment via actions in order to get maximum rewards in the short or long term. It does so by exploring the different possible actions and then modeling the once which leads to the maximum rewards.
How RL is different from the other ML domains
RL is one of the three basic paradigms of machine learning. The diagram below can help you easily visualize the key differences between these three domains
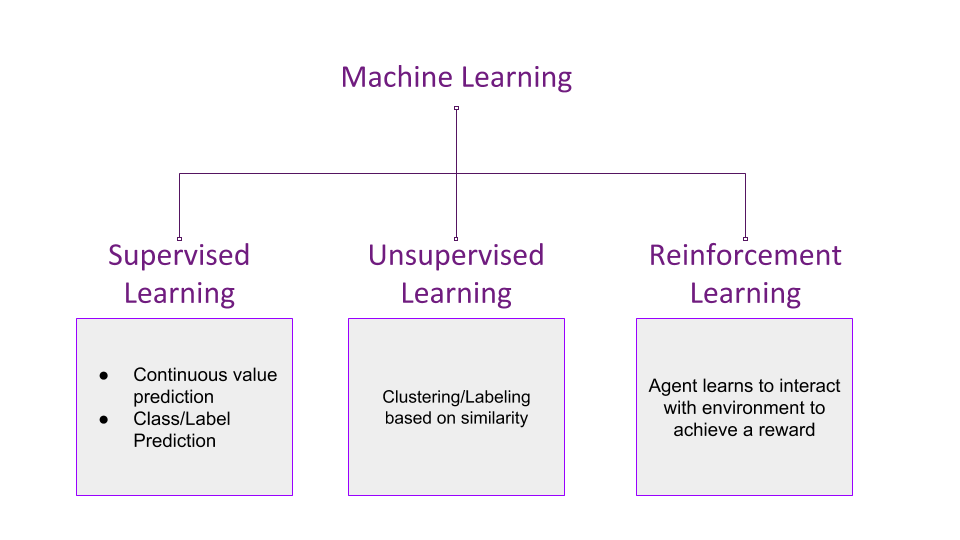
The one key difference between the supervised/unsupervised learning and re-enforcement learning is that in the former the whole datasets are present while the training process. But in the case of re-enforcement learning, you take actions and then the environment returns the consequences of your actions in the form of rewards. It resembles a “cause and effect” system. Hence this makes Re-enforcement Learning quite different from the other machine learning domains, in terms of training, etc.
Terminology used in Re-enforcement Learning
Here are some quick definitions of terms commonly used in RL. This is taken from the following source
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Agent | a hypothetical entity that performs actions in an environment to gain some reward. |
| Action (a) | All the possible moves that the agent can take. |
| Environment (e) | A scenario the agent has to face. |
| State (s) | Current situation returned by the environment. |
| Reward (R) | An immediate return sent back from the environment to evaluate the last action by the agent. |
| Policy (π) | The strategy that the agent employs to determine the next action based on the current state. |
| Value (V) | The expected long-term return with discount, as opposed to the short-term reward R. Vπ(s), is defined as the expected long-term return of the current state s under policy π. |
| Q-value or action-value (Q) | Q-value is similar to Value, except that it takes an extra parameter, the current action a. Qπ(s, a) refers to the long-term return of the current state s, taking action an under policy π. |
DIfferent Approaches used in RL
Majority of the RL algorithms can be classified into three major category,
Value Based
In a value-based reinforcement learning method, you try to maximize a value function V(s). As defined in the terminology previously, Vπ(s) is the expected long-term return of the current state s under policy π. Thus, V(s) is the value of reward which the agent expects to gain in the future upon starting at that state s.
Policy Based
In a policy-based reinforcement learning method, you try to come up with a policy such that the action performed at each state is optimal to gain maximum reward in the future. Here, no value function is involved. We know that the policy π determines the next action at any state s. There are two types of policy-based RL methods -
- Deterministic: at any state s, the same action is produced by the policy π.
- Stochastic: each action has a certain probability, given by P[ At = a | St = s]
Model Based
in this type of reinforcement learning, you create a virtual model for each environment, and the agent learns to perform in that specific environment. Since the model differs for each environment, there is no singular solution or algorithm for this type.
Inferences & Applications
RL is useful in many fields such as robotics, Logistics, game theory problems. A robot uses deep reinforcement learning to pick a device from one box and putting it in a container. Whether it succeeds or fails, it memorizes the object and gains knowledge and train’s itself to do this job with great speed and precision.
Reinforcement Learning and optimization techniques are utilized to assess the security of the electric power systems and to enhance Microgrid performance. Adaptive learning methods are employed to develop control and protection schemes. Transmission technologies with High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) and Flexible Alternating Current Transmission System devices (FACTS) based on adaptive learning techniques can effectively help to reduce transmission losses and CO2 emissions.
RL is changing our world in ways we can’t even imagine.